Fungal nail infections are among the most common conditions treated in podiatry. They can affect toenails, leading to discomfort and aesthetic concerns. Here is more information on fungal nails, their causes, symptoms, lifecycle, and treatment options:
What Are Fungal Nail Infections?
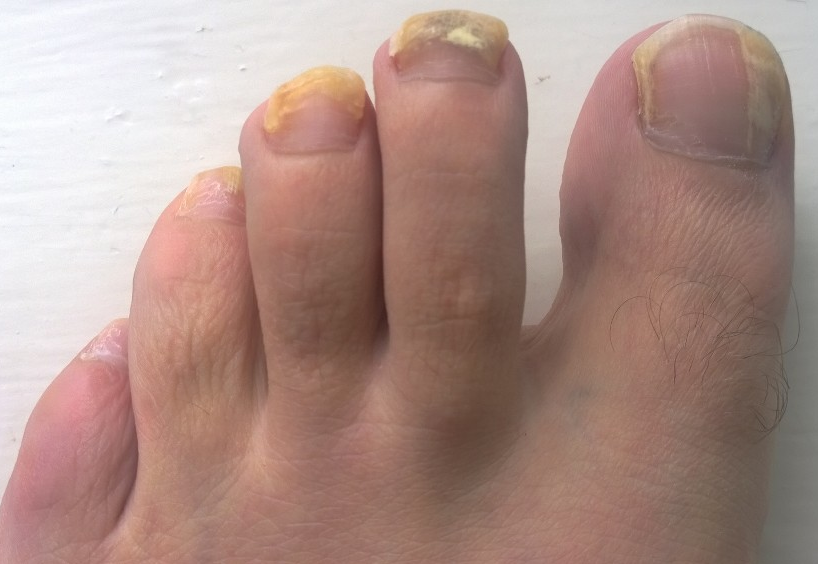
Fungal nail infections, also referred to as onychomycosis, occur when fungi infiltrate the nail or the surrounding tissue. They thrive in warm, moist environments and can affect individuals of all ages. The infection is typically visible on the nail, causing discoloration, thickening, or separation of the nail from the nail bed. Consulting a podiatrist helps diagnose and treat fungal nails affecting the toes.
What Causes Them?
Fungal nail infections develop when dermatophytes, molds, or yeasts invade the nail tissue. Shared spaces such as public pools, saunas, and gym showers are common sources of infection. Factors like improper nail hygiene, reduced immunity, or wearing tight-fitting shoes that trap moisture can increase susceptibility.
Nail trauma and underlying conditions, such as diabetes or peripheral vascular disease, can also raise the likelihood of developing this condition. People who frequently expose their nails to water may also face a higher risk. This includes swimmers or dishwashers.
What Are the Symptoms?
Fungal nail infections often begin subtly but progress if untreated. Symptoms include nails that:
- Appear yellow, white, or brown in color.
- Become brittle or crumbly, easily breaking or splitting.
- Grow thicker and develop an irregular texture.
- Separate from the nail bed completely in severe cases.
The infection may cause pain or discomfort, especially if the nail thickens to the point of pressing against the surrounding skin.
What Is the Lifecycle of Fungal Nail Infections?
The lifecycle of fungal nail infections begins with fungal spores coming into contact with the nail. These spores find an entry point through cracks, cuts, or minor injuries in or around the nail bed. Once inside, they multiply and create colonies that feed on keratin, a key structural protein of nails.
The infection typically begins in localized areas, often at the edge of the nail. It spreads deeper and wider across the nail plate over time. Fungi thrive under specific conditions, such as warmth and moisture, which allows the infection to persist and worsen without intervention. Understanding this lifecycle helps disrupt it with treatment.
What Are the Available Treatment Options?
Treatment for fungal nail infections varies depending on the severity and extent of the condition. Common approaches include:
- Antifungal Cream: Topical antifungal creams are designed to combat fungal growth on the nail. They are typically applied directly to the affected nail and surrounding skin.
- Oral Medication: Oral antifungal medications offer systemic treatment for moderate to severe infections. They target the fungi from within the body, limiting growth and clearing the infection.
- Laser Therapy: Laser therapy is a non-invasive option that uses concentrated light to eradicate fungal cells without damaging surrounding tissue. It may be viewed as a more convenient alternative to oral medication, particularly for individuals who cannot tolerate systemic drugs.
- Nail Removal Procedure: For persistent or advanced fungal infections, nail removal may be recommended. This procedure involves partial or complete removal of the affected nail to eliminate the infected tissue.
Treat Your Fungal Nails Today
Fungal nail infections rarely resolve on their own and can worsen over time if left untreated. Early detection and intervention can prevent complications and restore healthy nails efficiently. Seek professional care from a podiatrist to discuss the best treatment option for your condition. Address your fungal nail infection today and take the first step toward healthier, stronger nails.
- Choosing the Right Plastic Surgeon for Your Cosmetic Procedure
- Understanding Different Types of Laser Treatments for Skin Rejuvenation
- Why a Family Dentist is Key for Maintaining Oral Health
- The Benefits of Regular Visits to a Wellness Spa
- Exploring the Emotional and Psychological Triggers of Eating Disorders

Leave a Reply